As this is not really an expense of the business, Anushka is effectively being paid amounts owed to her as the owner of the business (drawings). The cash (asset) of the business will increase by $5,000 as will the amount representing the investment from Anushka as the owner of the business (capital). Let’s take a look at the formation of a company to illustrate how the accounting equation works in a business situation. Incorrect classification of an expense does not affect the accounting equation. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation. It can be defined as the total number of dollars that a company would have left if it liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities.
Example: How to Calculate the Accounting Equation from Transactions
- The accounting equation is a vital concept in accounting, underpinning financial reporting and analysis.
- For example, although the land cost $125,000, Edelweiss Corporation’s balance sheet does not report its current worth.
- For more insights into the accounting equation, consider enrolling in accounting courses or reading specialized literature.
- This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations.
One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. If a company keeps accurate records using the double-entry system, the accounting equation will always be “in balance,” meaning the left side of the equation will be equal to the right side. The balance is maintained because every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts.
Your Financial Accounting tutor
Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. The double-entry practice ensures that splitting payments to reconcile expenses in xero the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value. This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation.
Basic Accounting Equation Formula
A trade receivable (asset) will be recorded to represent Anushka’s right to receive $400 of cash from the customer in the future. As inventory (asset) has now been sold, it must be removed from the accounting records and a cost of sales (expense) figure recorded. The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25). The difference between the $400 income and $250 cost of sales represents a profit of $150. The inventory (asset) will decrease by $250 and a cost of sale (expense) will be recorded.
Accounting Equation Components
The balance of the total assets after considering all of the above transactions amounts to $36,450. It is equal to the combined balance of total liabilities of $20,600 and capital of $15,850 (a total of $36,450). Taking time to learn the accounting equation and to recognise the dual aspect of every transaction will help you to understand the fundamentals of accounting.
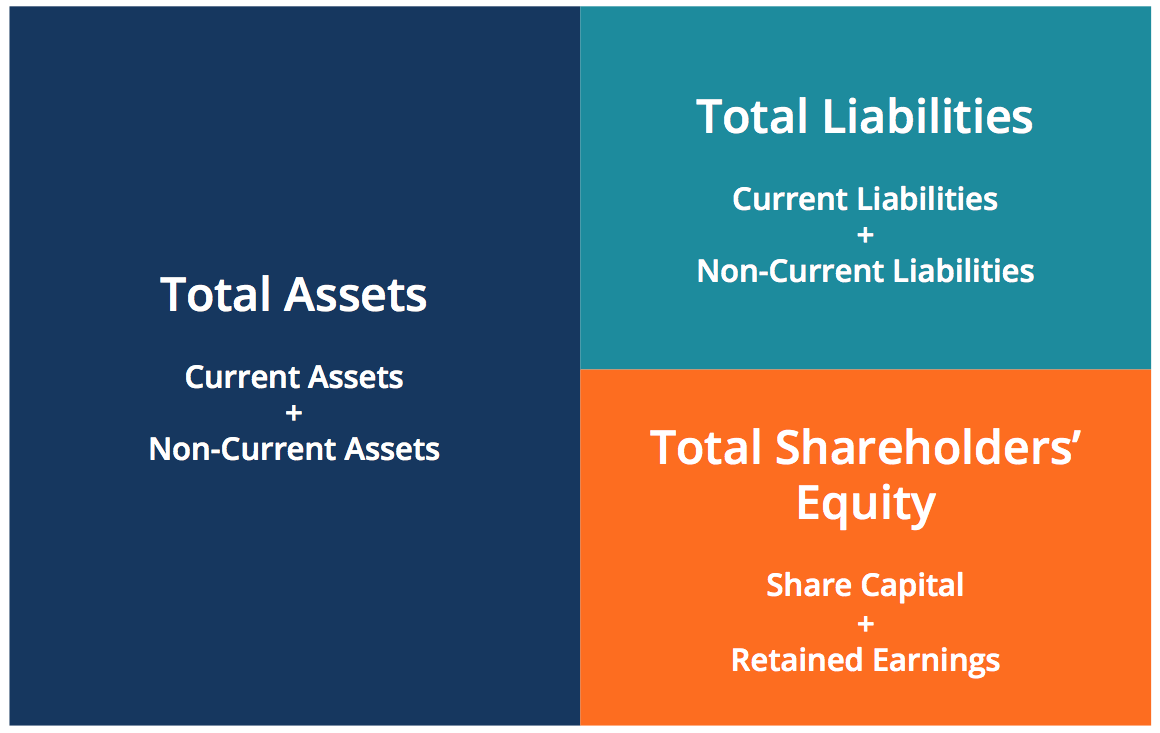
We know that every business holds some properties known as assets. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business. In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity. Current liabilities are obligations that a company needs to settle within one year. Examples include accounts payable and short-term loans.
If it’s financed through debt, it’ll show as a liability, but if it’s financed through issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll show in shareholders’ equity. Assets entail probable future economic benefits to the owner. In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash. At the same time, Capital increased due to the owner’s contribution. Remember that capital is increased by contribution of owners and income, and is decreased by withdrawals and expenses.
In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity. This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities. For example, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal increase to a related liability or shareholder’s equity account such that the accounting equation stays in balance. Alternatively, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal decrease in another asset account. It is important to keep the accounting equation in mind when performing journal entries. As business transactions take place, the values of the elements in the accounting equation change.
And these are going to be things like long term loans when we get a bank loan or bonds. Bonds is another way to raise money through loaning out through getting a loan, okay? So those are our liabilities and let’s go on to equity. Assets are a company’s resources—things the company owns. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill. From the accounting equation, we see that the amount of assets must equal the combined amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity.
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. An asset is considered current if it is for sale, if it can be realized within 12 month from the end of the accounting period or within the company’s normal operating cycle if it exceeds 12 months. In addition, cash is generally considered current asset.
The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions. All assets owned by a business are acquired with the funds supplied either by creditors or by owner(s). In other words, we can say that the value of assets in a business is always equal to the sum of the value of liabilities and owner’s equity. The total dollar amounts of two sides of accounting equation are always equal because they represent two different views of the same thing. The accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. This shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing.